Missouri Western State University 2006
From 2006.igem.org
(→'''Methods and Results''') |
(→'''Methods and Results''') |
||
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
Methods included synthetic DNA, PCR of natural genes, and reversal of existing parts. | Methods included synthetic DNA, PCR of natural genes, and reversal of existing parts. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Building new parts using synthetic DNA required that we determine the desired sequence, order the DNA to be made, anneal the oligos, ligate into pSB1A2, and verify using sequencing. This method was used to build the HixC, Recombination Enhancer (RE), and the Reverse RBS. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The process of PCR required us to locate the gene and design appropriate primers, isolate genomic DNA, work to optimize the PCR reaction, purify the band, and clone the gene into pSB1A2. This method was used to make Hin recombinase from Salmonella, Hin recombinase with an LVA tag, and three antibiotic resistance genes from E. coli. | ||
| + | |||
| + | To build reverse parts, we used a procedure that we affectionately call the PCR Switcharoo. Here, we designed the primers with the biobrick prefix and suffix switched. These primers were also complementary to the part. We purified the Xba1/Spe1 fragment of the part, amplified and purified the fragment, then cloned it into pSB1A2. We used this method to create the reversed pBAD promoter and three reversed antibiotic resistance genes. | ||
<big> <font color="blue">Basic Parts Made</font color> </big><br> | <big> <font color="blue">Basic Parts Made</font color> </big><br> | ||
| Line 106: | Line 112: | ||
<big> <font color="blue">Two pancake constructs </font color> </big><br> | <big> <font color="blue">Two pancake constructs </font color> </big><br> | ||
| - | Biological equivalence - distinguishing 1,2 from -2,-1 using RFP-RBS, updated panckaes | + | Biological equivalence - distinguishing 1,2 from -2,-1 using RFP-RBS, updated panckaes |
== '''Conclusions'''== | == '''Conclusions'''== | ||
Revision as of 02:10, 30 October 2006
See [http://www.flickr.com/search/?q=igem+missouri photos] from the Ambassador visit on June 5-6, 2006.
Contents |
Students
• Marian L. Broderick, senior mathematics major, [1]
• Adam D. Brown, senior biology major, [2]
• Trevor L. Butner, senior biochemistry/molecular biology major, [3]
• Lane H. Heard, Central High School (St. Joseph) senior, [4]
• Eric L. Jessen, senior biology major (health sciences), [5]
• Kelly J. Malloy, senior biology/chemistry major (health professions), [6]
• Brad J. Ogden, senior biology major (health sciences), [7]
Faculty
• Todd Eckdahl [http://staff.missouriwestern.edu/~eckdahl/], Professor, Department of Biology, [8]
• Jeff Poet [http://staff.missouriwestern.edu/~poet/], Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Science, Mathematics, and Physics, [9]
Shipping Address: Todd Eckdahl, Biology Department, Missouri Western State University, 4525 Downs Drive, Saint Joseph, MO, 64507 [(816) 271-5873]
Project Overview
Solving the Pancake Problem with an E. coli Computer
Our goal is to genetically engineer a biological system that can compute solutions to a puzzle called the burnt pancake problem. The EHOP computer is a proof of concept for computing in vivo, with implications for future data storage devices and transgenic systems. Our work was done in collaboration with the Davidson College iGEM team.
The Burnt Pancake Problem
The pancake problem is a puzzle in which a scrambled series of units (or stack of pancakes) must be shuffled into the correct order and orientation. In the burnt pancake problem, each pancake is given an orientation by burning one side. The The leftmost stack in Figure 1 below shows a scrambled stack of burnt pancakes. To solve the problem, every unit, or pancake, must be placed in the proper order (largest on bottom, smallest on top) and in the proper orientation (burnt side down, golden side up). The pancakes are flipped with two spatulas: one to lift pancakes off the top of the stack (if needed), the other to flip part (or all) of the remaining stack of pancakes. The pancakes lifted by the first spatula are returned to the top of the stack without being flipped. The illustration below shows that this stack of pancakes can be put into correct order and orientation in three such steps. One can verify that no two allowable flips are sufficient. Mathematically, one question sorrounding this scenario is to determine the least number of allowable two-spatula flips needed to change a given arrangement of pancakes into the correct order and orientation.
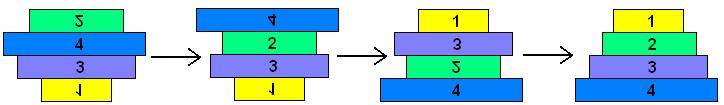
Approach
Trial and error is one approach to solving the burnt pancake problem, but how could one compute the quickest solution? Our idea is to let E. coli do the work, using each cell as a tiny processor in a massively parallel machine. A mathematical model of the flipping process helps us design the system and interpret the output of our EHOP computer.
Biological System
The biological representation of a pancake is a functional unit of DNA such as a promoter or coding region. To flip these units of DNA, we have reconstituted the Hin/ Hix invertase system from Salmonella typhimurium as a BioBrick compatible system in E. coli. Hin invertase (BBa_J31001) was cloned from S. typhimurium, Ames strain TA100 and tagged with LVA. We built the recombinational enhancer (RE) and Hin invertase recognition sequence HixC using the publicly available genomic sequence of S. typhimurium and a dsDNA assembly program we created for gene synthesis from overlapping oligos.
Every segment of DNA flanked by a pair of HixC sites is a "pancake" capable of being inverted. Hin invertase recognizes pairs of HixC sites and inverts the DNA fragment in between the two HixC sites with the help of the Fis protein bound to the RE. In our system, selectable phenotypes (including antibiotic resistance and RFP expression), depend upon the proper arrangement of a series of HixC-flanked DNA segments in a plasmid. This allows us to select for cells that have successfully solved the puzzle.
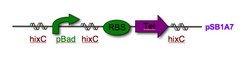 Figure 2 A sorted stack of two biological "pancakes"
Figure 2 A sorted stack of two biological "pancakes"
Mathematics
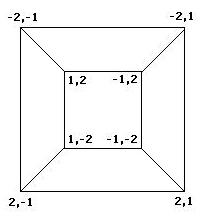
To better understand the possible results of the flipping of biological pancakes, it was necessary to better understand the combinatorial mathematics underlying the process. For a burnt pancake problem involving n pancakes, there are n!2^n possible orders and orientations of the pancakes. A graph representing the relationships between the 8 orders and orientations of two pancakes is given if Figure 3 below. This is useful in understanding "how close" one stack is to another. For example, if a stack begins as -2,1 and ends in the final position of 1,2, then we know AT LEAST two flips took place, although we can not determine exactly which flips or how many. The flipping of a stack from an initial position to the final position corresponds to what is called a walk in the graph.
Figure 3: Relationships among stacks of two pancakes
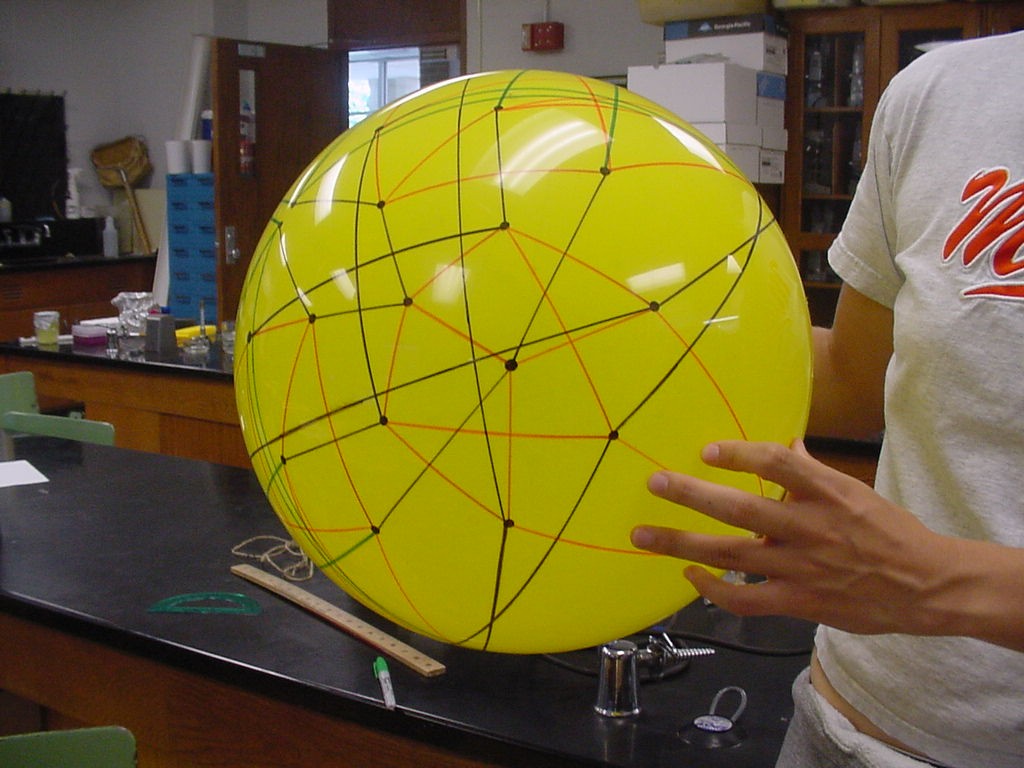
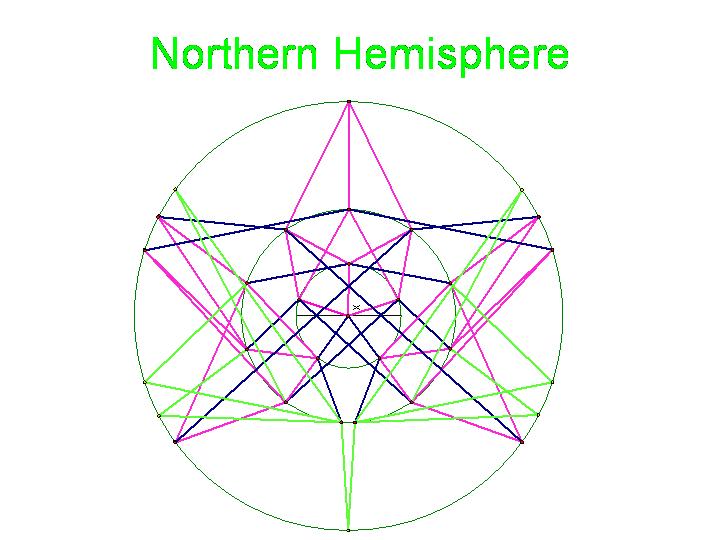
Note that there are 48 possible stacks of three burnt pancakes. While this graph is far more unwieldy, we were able to model this graph on a sphere. Figure 4 below illustrates the view of the sphere from the "North Star". The graph below has one vertex at the North Pole, five vertices on the Arctic Circle, eleven vertices on the Tropic of Capricorn, and fourteen vertices on the Equator. The southern hemisphere is an inversion of this graph. Figure 5 is a picture of the full graph with 48 vertices on a sphere representing the 3-pancake problem.
Figure 4a: Northern Hemisphere
Figure 4b: Anyone else see DaVinci's Vitruvian Man in this, or is it just us?
Figure 5: Full graph of the 3-burnt pancake problem
A population of E. coli cells (1015 cells, for instance) each carrying ~100 copies of pancake stacks has astounding parallel processing capacity.
Methods and Results
Building New Parts
Methods included synthetic DNA, PCR of natural genes, and reversal of existing parts.
Building new parts using synthetic DNA required that we determine the desired sequence, order the DNA to be made, anneal the oligos, ligate into pSB1A2, and verify using sequencing. This method was used to build the HixC, Recombination Enhancer (RE), and the Reverse RBS.
The process of PCR required us to locate the gene and design appropriate primers, isolate genomic DNA, work to optimize the PCR reaction, purify the band, and clone the gene into pSB1A2. This method was used to make Hin recombinase from Salmonella, Hin recombinase with an LVA tag, and three antibiotic resistance genes from E. coli.
To build reverse parts, we used a procedure that we affectionately call the PCR Switcharoo. Here, we designed the primers with the biobrick prefix and suffix switched. These primers were also complementary to the part. We purified the Xba1/Spe1 fragment of the part, amplified and purified the fragment, then cloned it into pSB1A2. We used this method to create the reversed pBAD promoter and three reversed antibiotic resistance genes.
Basic Parts Made
Parts constructed in this project by the Missouri Western and Davidson iGEM teams:
http://partsregistry.org/cgi/partsdb/pgroup.cgi?pgroup=iGEM2006partsregistry.org/cgi/partsdb/pgroup.cgi?pgroup=iGEM2006&group=Missouri
Flipping DNA
One pancake and two pancake constructs were made and tested for flipping. Restriction mapping was used to verify that flipping was occuring in one pancake constructs. Since in these experiments the Hin recombinase expression cassette had not be intentionally induced, the flipping was occurring spuriously.
Additional experiments are underway to measure flipping genetically with Tet resistance and to test two pancake constructs.
Modeling
Modeling the behavior of pancake flipping: deducing kinetics and size biases Using modeling to choose which families of unsolved pancake stacks to start with Building the Biological System
Single pancakes
The problems of read-through - uncontrolled Tet expression, uncontrolled flipping
New pSB1A7 vector: insulates, but is not compatible with parts carrying double terminators
Designing pancakes without TT's
Two pancake constructs
Biological equivalence - distinguishing 1,2 from -2,-1 using RFP-RBS, updated panckaes
Conclusions
Consequences of devices: data storage, possible application for rearranging transgenes in vivo, proof-of-concept for bacterial computers, first in vivo controlled flipping of DNA?? Next steps: can solve problem but need control over kinetics Lessons learned: Troubleshooting, communication, teamwork, publicity Math and Biology meshed really well and even uncovered a new proof Multiple campuses can increase capacity through communication and cooperation Size of school is not a limiting factor We had a blast and learned heaps
Retrieved from "http://partsregistry.org/cgi/partsdb/pgroup.cgi?pgroup=iGEM2006partsregistry.org/cgi/partsdb/pgroup.cgi?pgroup=iGEM2006&group=Missouri"
Assembly Plan
Math Stuff
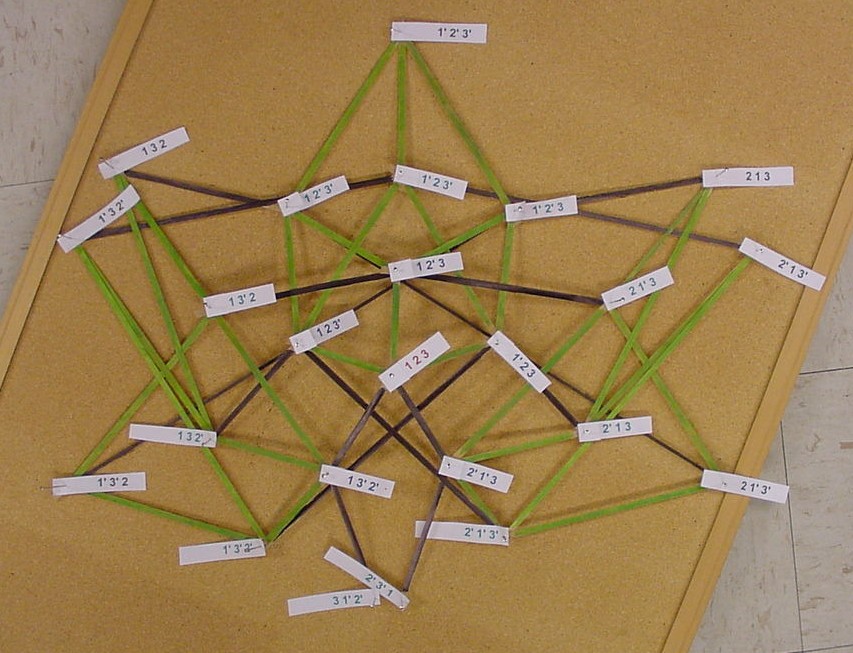
The picture below is of the half graph for the signed permutations for the 3-pancake problem. The full graph would have 48 vertices with each connected to six other vertices. The plan is to transfer this half graph onto the northern hemisphere of a globe with 123 as the north pole, five permutations on the Arctic Circle, eleven on the Tropic of Capricorn, and seven on the equator. An identical graph can be placed on the southern hemisphere such that each permutation occurs diametrically opposite its biological complement. In the picture below, green edges correspond to flips involving one pancake only and black edges correspond to a flip in which a double pancake is involved.
The graphic below was created using Geometer's SketchPad by Marian and shows the 24 vertices on the Northern Hemisphere, similar to the pushpin and rubber band manipulative above. The edges in this graph represent the relationships among the permutations. Pink edges correspond to the flip of a single pancake, black edges to the flip of a double, and green edges to vertices in the Southern Hemisphere. A 3-D model on a globe (okay, it is really a beachball) is in progress. Of curious note, doesn't this graph look similar to Da Vinci's Vitruvian Man?
This image is the connected graph of forty-eight vertices on a sphere....finally!
Publicity
MWSU Tower Topics [http://staff.missouriwestern.edu/~eckdahl/iGEM/Tower_Topics_7_2006.htm]
St. Joseph News-Press [http://staff.missouriwestern.edu/~eckdahl/iGEM/St_Joseph_NewsPress_7_2006.htm]
Research Links
OWW Protocols [http://openwetware.org/wiki/Protocols]
Source Plates [http://2006.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Biobrick_delivery&printable=yes]
Goodman et al. 1973-1979. The Pancake Problems [http://www.math.uiuc.edu/~west/openp/pancake.html]
Nanassy and Hughes. 1998. In Vivo Identification of Intermediate Stages of the DNA Inversion Reaction Catlyzed by the Salmonella Hin Recombinase [http://www.genetics.org/cgi/content/abstract/149/4/1649]
Lim et al. 1997. Hin-mediated Inversion on Positively Supercoiled DNA [http://www.jbc.org/cgi/content/full/272/29/18434]
Hughes et al. 1992. Sequence-specific interaction of the Salmonella Hin recombinase in both major and minor grooves of DNA [http://www.pubmedcentral.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pubmed&pubmedid=1628628]
Nanassy and Hughes. 2001. Hin Recombinase Mutants Functionally Disrupted in Interactions with Fis [http://jb.asm.org/cgi/content/full/183/1/28?view=long&pmid=11114897]
Lee et al. 1998. In Vivo Assay of Protein-Protein Interactions in Hin-Mediated DNA Inversion [http://jb.asm.org/cgi/content/abstract/180/22/5954]
Merickel et al. 1998. Communication between Hin recombinase and Fis regulatory subunits during coordinate activation of Hin-catalyzed site-specific DNA inversion [http://www.genesdev.org/cgi/content/abstract/12/17/2803]
Haykinson and Johnson. 1993. DNA looping and the helical repeat in vitro and in vivo: effect of HU protein and enhancer location on Hin invertasome assembly [http://www.pubmedcentral.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pubmed&pubmedid=8508775]
Vasquez et al. 2004. Tangle Analysis of Gin Site-specific Recombination [http://math.berkeley.edu/~mariel/Vazquez_Gin04.pdf]
Merickel and Johnson. 2004. Topological analysis of Hin-catalysed DNA recombination in vivo and in vitro [http://www.blackwell-synergy.com/doi/abs/10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03890.x]
R.C. Johnson and M.F. Bruist. 1989. Intermediates in Hin-mediated DNA inversion: a role for Fis and the recombinational enhancer in the strand exchange reaction [http://www.pubmedcentral.gov/picrender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&blobtype=pdf&artid=400990]
Lim and Simon. 1992. The Role of Negative Supercoiling in Hin-mediated Site-Specific Recombination[http://www.jbc.org/cgi/content/abstract/267/16/11176]
The Pancake Tossing World Record[http://www.recordholders.org/en/records/pancake.html]
Cool site for Breakfast [http://www.cut-the-knot.org/SimpleGames/Flipper.shtml]
iGEM iDeas
Powerpoint with two possible project ideas. [http://staff.missouriwestern.edu/~eckdahl/Research/Synthetic_Biology_2006/IGEMideas%2005-29-06.ppt]