ETH Zurich 2006
From 2006.igem.org
(→system deployment) |
m (→design process: rephrasing and other language corrections) |
||
| Line 95: | Line 95: | ||
After the proposals, we decided to further pursue the half adder project idea. | After the proposals, we decided to further pursue the half adder project idea. | ||
| - | == | + | == Design process == |
| - | === | + | === System behavorial specification === |
# Write something with a chemical on a petri plate (like '''ETH''' for example) | # Write something with a chemical on a petri plate (like '''ETH''' for example) | ||
| Line 118: | Line 118: | ||
| - | + | An experiment in the lab could for instance look like this: | |
| Line 124: | Line 124: | ||
| - | + | or like this: | |
| Line 133: | Line 133: | ||
The whole system is only considered at it's steady state, dynamic processes are only of minor interest. | The whole system is only considered at it's steady state, dynamic processes are only of minor interest. | ||
| - | === | + | === System structure === |
The whole process can be brought into a common input, logic, output form: | The whole process can be brought into a common input, logic, output form: | ||
| Line 141: | Line 141: | ||
[chemical sensing]-->[ ]-->[reporter B] | [chemical sensing]-->[ ]-->[reporter B] | ||
| - | As it turns out, a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Full_adder half-adder] can be used as logic part. A half adder can add 2 binary values and thus has 2 inputs. It has also 2 outputs, the sum value S and a carry out C | + | As it turns out, a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Full_adder half-adder] can be used as logic part. A half adder can add 2 one bit binary values and thus has 2 inputs. It has also 2 one bit outputs, the sum value S and a carry out C. Two half-adders can be combined to a full-adder, which computes the two bit sum of three one bit numbers (the two operands and the carry from the next less significant bit). |
A half adder can be constructed from an XOR gate (the sum value S) and an AND gate (the carry out): | A half adder can be constructed from an XOR gate (the sum value S) and an AND gate (the carry out): | ||
| Line 154: | Line 154: | ||
S = A XOR B C = A AND B | S = A XOR B C = A AND B | ||
| - | + | The sum output S and the carry out C are exactly the values needed for our system. The resulting system architecture is: | |
[[image:ETH_System_Architecture.png|center| |system architecture]] | [[image:ETH_System_Architecture.png|center| |system architecture]] | ||
| Line 164: | Line 164: | ||
* [[ETH2006_copy| pops duplexer]] | * [[ETH2006_copy| pops duplexer]] | ||
| - | === | + | === System modeling === |
| - | + | According to the system structure, we first decompose our overall system into devices: | |
* [[ETH2006_xor| xor gate]] | * [[ETH2006_xor| xor gate]] | ||
* [[ETH2006_and| and gate]] | * [[ETH2006_and| and gate]] | ||
| Line 172: | Line 172: | ||
* [[ETH2006_light| light sensing]] | * [[ETH2006_light| light sensing]] | ||
* [[ETH2006_copy| pops duplexer]] | * [[ETH2006_copy| pops duplexer]] | ||
| - | + | Every devices dynamic behavior was modeled by a set of odes (ordinary differential equations). The steady-state we are interested in was determined by simulating the system until all the states (concentrations and rates) settled down to rather constant values. This method is not mathematically sound as systems might settle to different steady-states depending on the initial conditions, or the system might regain momentum after almost, but no completely, settling down. The first concern can be adressed by running simulations starting from varying initial conditions and verifying that there is only a single steady-state, the second issue is rather theoretical as this kind of behaviour is rarely found in real systems. | |
| - | ==== | + | ==== Modular simulation ==== |
| - | + | Modular modeling allows simulation at different detail levels, e.g. | |
* single devices, different variants of same device type, as a basis of decisionmaking | * single devices, different variants of same device type, as a basis of decisionmaking | ||
* reusable complexes reoccurring in different devices, like | * reusable complexes reoccurring in different devices, like | ||
| Line 184: | Line 184: | ||
* overall system → to see if everything together still works | * overall system → to see if everything together still works | ||
| - | + | We have developed such a modular system in MATLAB: | |
* the current implementation defines modules at device level (reusable complexes is a pending issue) | * the current implementation defines modules at device level (reusable complexes is a pending issue) | ||
* modules mainly are characterized by number/kind of input and output and can be simulated with an appropriate simulation function | * modules mainly are characterized by number/kind of input and output and can be simulated with an appropriate simulation function | ||
| Line 190: | Line 190: | ||
* the modules have 1-2 inputs/ouptus, for instance 2 inputs/1 ouptut for AND/XOR gate | * the modules have 1-2 inputs/ouptus, for instance 2 inputs/1 ouptut for AND/XOR gate | ||
| - | ==== | + | ==== Parameter estimation & sensitivity analysis ==== |
| - | + | It is known, and we have made the same (sometimes painful) experience that parameter estimation is the most difficult and laborious part of modeling. Most parameters are simply not known, and estimating them sometimes approaches playing dice. | |
| - | + | One way to address this problem is sensitivity analysis: if we change some parameter, what effect has it on the behavior of the model? The sensitivity matrix S at steady state can be computed with the jacobian matrices of the ODEs with respect to the states (concentrations) and parameters. To be able to compare the results, parameter and state values are normalized, that is, the changes are expressed relative to the unperturbed value. | |
| - | + | Sensitivity analysis gives clues about | |
| - | * | + | * whether our models behaviour resembles the desired behavior |
| - | * | + | * which parameters have hardly any effect on the relevant states (they don't have to be considered further and can be fixed to some arbitary value) |
| - | * | + | * which parameters influence the relevant states significantly and thus deserve further attention |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | ==== | + | ==== The role of modeling ==== |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | With all the uncertainties and difficulties (such as parameter estimation) the question might raise whether modeling is worthwile at all. Our answer is yes, but one has to think of modeling as an integrated process. It should not be seen as a precursor phase of experiment and synthesis, it is part of the design cycle. | |
| - | + | After brainstorming and selecting a project, we started with abstract models of the necessary devices on a very schematic level. For instance, we came up with different theoretical models for the XOR and AND gates - without considering biology too much at this early stage. Then we looked for biological systems which resembled one of our models - the literature research was to some extent model driven. We refined the remaining models and simulated the devices for the first time - here, the ODEs and MATLAB joined in. These models helped a lot in deciding which gate variants should be prefered. As we gained knowledge about possible biological implementations, the models where constantly adapted. | |
| + | Important is also the interaction of modeling and experiments. Modeling and sensitivity analysis can suggest where observed difficulties arise and thus guide the experiments that pin down the problem, eventually leading to a solution. | ||
| - | + | === System deployment === | |
| - | === | + | |
We will assembly the and gate plus the xor gate on two seperate plasmids (pACYC177 and pACYC184 from NEB). In order for our system to be tested we need a special strain expressing lacI and tetR. In our case we plan to use strain DH5αZ1. | We will assembly the and gate plus the xor gate on two seperate plasmids (pACYC177 and pACYC184 from NEB). In order for our system to be tested we need a special strain expressing lacI and tetR. In our case we plan to use strain DH5αZ1. | ||
| - | === | + | === System assembly procedure === |
''to be done'' | ''to be done'' | ||
| - | === | + | === System test procedure === |
''to be done'' | ''to be done'' | ||
Revision as of 09:48, 29 October 2006

standing (L-R): Marco, Alexandra, Arthur, Olga, Dimo, Marko, Robert; in front (L-R):
Adding numbers is easy, isn't it? 1234 plus 5678, for example, is 6912. But how do engineers add binary numbers instead of decimal ones? And how, in the end, can this be done by a living cell? We, the members of the ETH Zurich 2006 iGEM team, are currently working on these questions, whereas the last one seems to be not trivial.
What the addition of numbers has to do with pattern recognition, how our model and the mathematical analysis look like, and how the experiments are realized will be explained on these wiki pages. We wish you a pleasant time with our pages. Enjoy it!
Contents |
Coordination
TODOs
Modeling
- Parts Model the whole System with Sensing, Pops duplexer and Half adder (Marco and Franz) -- probably not
- Model whether a different strength of input is necessary for the AND and XOR Gates (Marco)
- Finish modeling the second AND Gate and find a biological way to implement it and write the DNA and order it (Marco and Robert) -- probably not
- Bring model parameter up to date & update simulation results/senisitivity analysis (Marco)
Lab
Responsible: Robert for the preparatory experiments, Olga for the assembly and testing of the gates.
- Read the literature on the XOR and AND Gates, check carefully for strains needed and compatibility of the parts (Who?)
- Prepare a protocol for parts assembly (Olga)
- Assembly of the chemical sensing device (Franz, Dimo, Robert, Marco, Marko, Olga) DONE
- Test chemical sensing device DONE?
Documentation
Responsible: Alexandra for the registry, Arthur for the Wiki.
- enter lab experience report to registry
- Make a drawing of the DNA to have an overview of which parts will be consecutively on the same DNA piece (Alexandra) (this is part of the #system deployment section --Ajk)
- Revise images & graphics (Marco):
- correct errors
- unify symbols
- extract missing ones from slides, see here
Presentation/Poster and PR
Responsible: Franz for the presentation, Dimo for PR/Poster
- design and write the final presentation (with LaTex beamer class) IN PROCESS
- draw a team logo and find a team name (Franz and Dimo)
- design and order T-Shirts (Dimo)
- setup poster (Dimo), collect info/distribute tasks
Structure:
1. Introduction of the team and ETH Zurich and of the half-adder idea - about 3 min
2. Engineering Part - about 9 min
3. Biological part - about 8 min
(4.) Questions from the audience - 10min (I think, Marco (modelling) and Marko (biology) should also be ready to answer questions)
Schedule
Available as Google Calendar: [http://www.google.com/calendar/render?cid=pqi8ni6gnfj5r3o0np0h4smrr4@group.calendar.google.com iGEM 2006 ETH Zurich]
- past
- see here
- 30.10.
- Project documentation on the Wiki has to be complete
- 4./5.11.
- Jamboree in Boston
Participants and availability
- Michael Friedmann:
- Dimo Brockhoff:
- Franz Zürcher:
- Olga Nikolayeva:
- Alexandra Choutko:
- Arthur Korn:
- Robert Schütz:
- Marco Terzer:
- Marko Jovanovic:
Finding a Project
Finding a project to work on is not easy. Not because it is hard to find interesting projects but because there are too many of them. In the first weeks we did a lot of brainstorming including thoughts about the projects' feasibility. You can find a list of ideas here.
During the weeks, we decided to split up the whole team into two groups. Each group proposed a project after these two weeks of separated work:
- Meat monitor project (Michael, Dimo, Olga, Arthur, Marko)
- Half adder/pattern recognition project (Franz, Alexandra, Robert, Marco)
After the proposals, we decided to further pursue the half adder project idea.
Design process
System behavorial specification
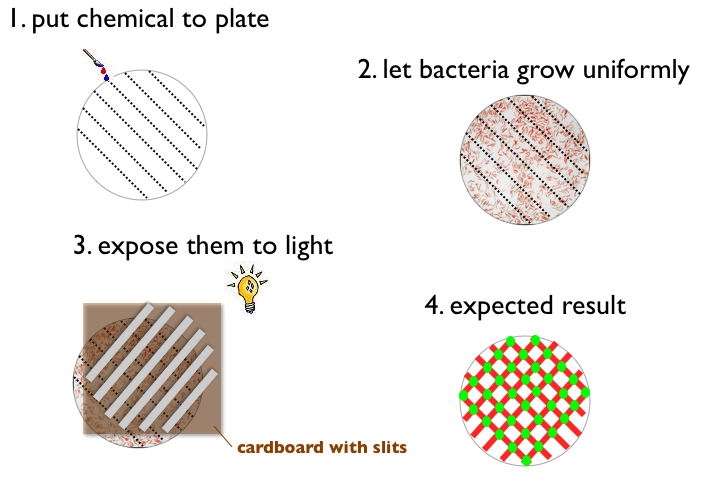
- Write something with a chemical on a petri plate (like ETH for example)
- Let Bacteria grow uniformly on the plate
- Expose the plate to a picture (black and white) of the same pattern
- Result:
- Bacteria gets green when pattern on the plate and picture match (light and chemical)
- Bacteria does not express fluorescent protein when pattern on the plate and picture match (no light and no chemical)
- Bacteria gets red when pattern on the plate and picture do not match
light no light chemical A B no chemical B C
The outputs can be reported by fluorescent proteins, the mapping of states to outputs is arbitary, our choice is:
A: green B: red C: no fluorescence
An experiment in the lab could for instance look like this:
or like this:
Considering the green and the red output as being separate, the logic mapping the input states to the output states is AND for the GFP and XOR for the RFP. Together they amount to a half adder logic.
The whole system is only considered at it's steady state, dynamic processes are only of minor interest.
System structure
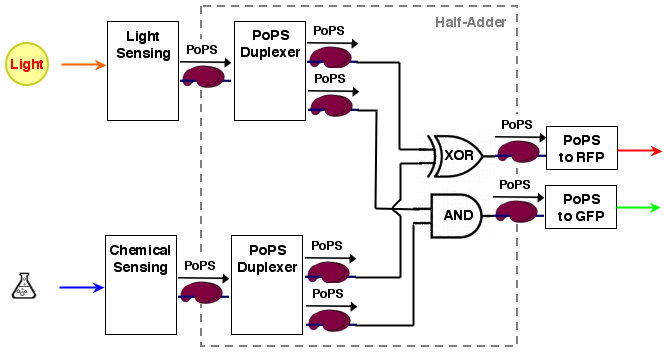
The whole process can be brought into a common input, logic, output form:
[light sensing]----->[ ]-->[reporter A]
[ logic ]
[chemical sensing]-->[ ]-->[reporter B]
As it turns out, a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Full_adder half-adder] can be used as logic part. A half adder can add 2 one bit binary values and thus has 2 inputs. It has also 2 one bit outputs, the sum value S and a carry out C. Two half-adders can be combined to a full-adder, which computes the two bit sum of three one bit numbers (the two operands and the carry from the next less significant bit).
A half adder can be constructed from an XOR gate (the sum value S) and an AND gate (the carry out):
A A
^ ^
1| 1 0 1 | 0 1
0| 0 1 0 | 0 0
+-----> B +----> B
0 1 0 1
S = A XOR B C = A AND B
The sum output S and the carry out C are exactly the values needed for our system. The resulting system architecture is:
System modeling
According to the system structure, we first decompose our overall system into devices:
Every devices dynamic behavior was modeled by a set of odes (ordinary differential equations). The steady-state we are interested in was determined by simulating the system until all the states (concentrations and rates) settled down to rather constant values. This method is not mathematically sound as systems might settle to different steady-states depending on the initial conditions, or the system might regain momentum after almost, but no completely, settling down. The first concern can be adressed by running simulations starting from varying initial conditions and verifying that there is only a single steady-state, the second issue is rather theoretical as this kind of behaviour is rarely found in real systems.
Modular simulation
Modular modeling allows simulation at different detail levels, e.g.
- single devices, different variants of same device type, as a basis of decisionmaking
- reusable complexes reoccurring in different devices, like
- transcription
- translation
- encymatic reactions
- 2 or several connected devices → for instance to see which duplexer variant fits better with which AND/XOR gate variant
- overall system → to see if everything together still works
We have developed such a modular system in MATLAB:
- the current implementation defines modules at device level (reusable complexes is a pending issue)
- modules mainly are characterized by number/kind of input and output and can be simulated with an appropriate simulation function
- input/output kind: we destiguish between concentration and rate (PoPS)
- the modules have 1-2 inputs/ouptus, for instance 2 inputs/1 ouptut for AND/XOR gate
Parameter estimation & sensitivity analysis
It is known, and we have made the same (sometimes painful) experience that parameter estimation is the most difficult and laborious part of modeling. Most parameters are simply not known, and estimating them sometimes approaches playing dice.
One way to address this problem is sensitivity analysis: if we change some parameter, what effect has it on the behavior of the model? The sensitivity matrix S at steady state can be computed with the jacobian matrices of the ODEs with respect to the states (concentrations) and parameters. To be able to compare the results, parameter and state values are normalized, that is, the changes are expressed relative to the unperturbed value.
Sensitivity analysis gives clues about
- whether our models behaviour resembles the desired behavior
- which parameters have hardly any effect on the relevant states (they don't have to be considered further and can be fixed to some arbitary value)
- which parameters influence the relevant states significantly and thus deserve further attention
The role of modeling
With all the uncertainties and difficulties (such as parameter estimation) the question might raise whether modeling is worthwile at all. Our answer is yes, but one has to think of modeling as an integrated process. It should not be seen as a precursor phase of experiment and synthesis, it is part of the design cycle.
After brainstorming and selecting a project, we started with abstract models of the necessary devices on a very schematic level. For instance, we came up with different theoretical models for the XOR and AND gates - without considering biology too much at this early stage. Then we looked for biological systems which resembled one of our models - the literature research was to some extent model driven. We refined the remaining models and simulated the devices for the first time - here, the ODEs and MATLAB joined in. These models helped a lot in deciding which gate variants should be prefered. As we gained knowledge about possible biological implementations, the models where constantly adapted.
Important is also the interaction of modeling and experiments. Modeling and sensitivity analysis can suggest where observed difficulties arise and thus guide the experiments that pin down the problem, eventually leading to a solution.
System deployment
We will assembly the and gate plus the xor gate on two seperate plasmids (pACYC177 and pACYC184 from NEB). In order for our system to be tested we need a special strain expressing lacI and tetR. In our case we plan to use strain DH5αZ1.
System assembly procedure
to be done
System test procedure
to be done
In order to test the functionality of the gates experimentally, we decided to mimic the signal inputs via two well controllable inducible promoters. This will help us to test the gates under different input conditions and help in determining the limits of our system. As inducible promoters we chose the lactose-inducible promoter (Plac) and the tetracycline-inducible promoter (Ptet). Both promoters are well described in literature and also tested extensively. However, in order to test our system with those two promoters, we will need to use a special e. coli strain, designed our whose genome encodes for the tetR and lacI gene (e.g. DH5αZ1 strain). The two promoters are flanked by unique restriction sites, so that once the gates are tested, these promoters can be easily exchanged by any promoter of interest. Consequently, our gates could be coupled to a number of other promoters that respond to a desired input signal.