PLac Tet Pancake Plan
From 2006.igem.org
(→pLac Tet Pancake Assembly Plan) |
|||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
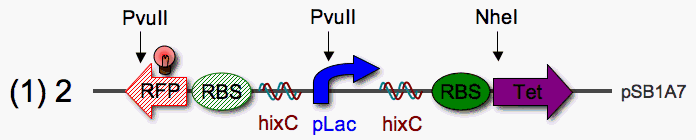
<b>Restriction Mapping</b>: PvuII sites occur once in the stationary RFP reporter and once in pLac. A PvuII digest can be used to check the orientation of pLac anywhere in the stack. Since PvuII and NheI share optimal buffers (Promega), a simple double digest could be used to check the orientation of the Tet pancake. | <b>Restriction Mapping</b>: PvuII sites occur once in the stationary RFP reporter and once in pLac. A PvuII digest can be used to check the orientation of pLac anywhere in the stack. Since PvuII and NheI share optimal buffers (Promega), a simple double digest could be used to check the orientation of the Tet pancake. | ||
| - | <b>Construction, Step 1</b>: | + | <b>Construction, Step 1</b>: First, I will build a hix-flanked pLac promoter (pLac single pancake) with a reverse RBS-RFP to the left and RBS-TetF to the right. If pLac can read through hix, the cells will be tetracycline resistant. |
| + | |||
| + | <b>Construction, Step 2</b>: Next, I will cotransform the pLac single pancake construct with the Hin-LVA expression cassette and induce Hin expression with IPTG. Flipping should yeild constructs with reverse pLac promoters resulting in RFP expression. Successful flipping will indicate that Hin can invert a strong promoter. | ||
Revision as of 20:03, 19 February 2007
pBad Is a Weak Promoter
In our previous design, we aniticpated that a reverse RBS-RFP reporter would distinguish the biologically equivalent (1, 2) and (-2, -1) configurations of a pBad, TetR two-pancake stack. To test this, I placed the reverse RBS-RFP reporter to the left of (-2, -1). I also placed it to the left of (-1, -2) to see if the distance between the pBad promoter and the RFP would affect expression.
Only RFPrev-RBSrev-(-1, -2) confers weak expression of RFP (faint pink cell pellet), even after 0.2 - 2.0% arabinose induction in the absence of an extragenic copy of AraC (repressor of pBad). This result suggests that JM109 cells have endogenous AraC that represses pBad and that pBad is a weak promoter that requires close proximity to its coding region. Since one of our goals is to build long multi-coding sequence pancake stacks, pBad is a poor choice for this device (but may be useful in controlling Hin expression).
pLac Tet Pancake Assembly Plan
We've observed that pLac promotes strong expression of RBS-RFP, even in the absence of an inducer (IPTG). pLac may be better suited for our pancake stack device.
Restriction Mapping: PvuII sites occur once in the stationary RFP reporter and once in pLac. A PvuII digest can be used to check the orientation of pLac anywhere in the stack. Since PvuII and NheI share optimal buffers (Promega), a simple double digest could be used to check the orientation of the Tet pancake.
Construction, Step 1: First, I will build a hix-flanked pLac promoter (pLac single pancake) with a reverse RBS-RFP to the left and RBS-TetF to the right. If pLac can read through hix, the cells will be tetracycline resistant.
Construction, Step 2: Next, I will cotransform the pLac single pancake construct with the Hin-LVA expression cassette and induce Hin expression with IPTG. Flipping should yeild constructs with reverse pLac promoters resulting in RFP expression. Successful flipping will indicate that Hin can invert a strong promoter.