MIT 2006
From 2006.igem.org
This page is a summary of the work done by the MIT 2006 iGEM team. Much more information is available on [http://openwetware.org/wiki/IGEM:MIT/2006 OpenWetWare].
Members
The MIT iGEM team has 5 undergraduates, 5 graduate student advisors, and 2 faculty advisors (figure 1).
|
|
Email us: team AT igem.mit.edu
Project description
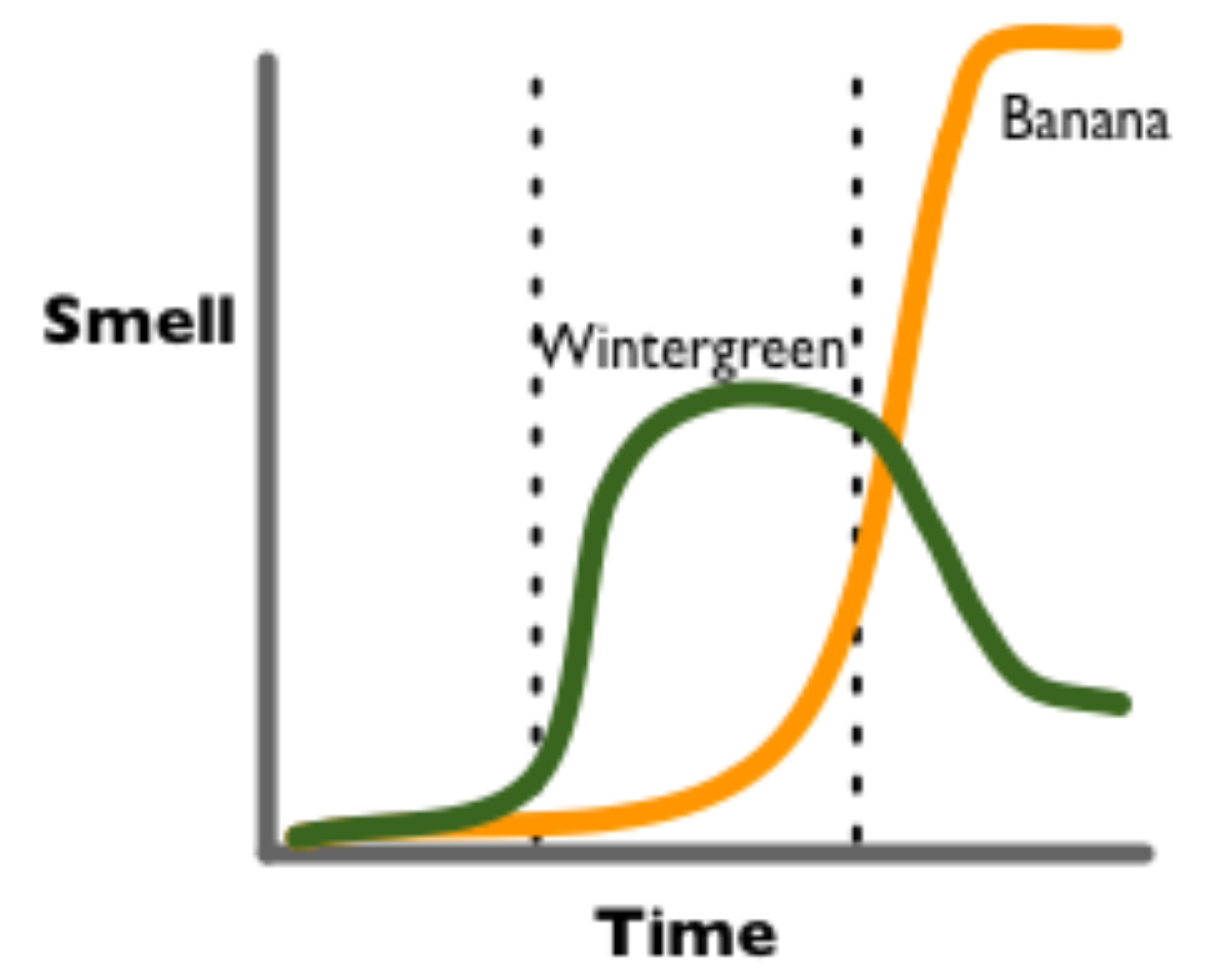
This summer, MIT's iGEM 2006 team engineered Escherichia coli to produce a wintergreen scent during exponential phase and a banana scent during stationary phase using only endogenous metabolites (figure 2). Thus, our project demonstrates that
- It is indeed possible to design, build and test a synthetic biological system over the course of a summer.
- Biosynthetic devices that produce scented compounds can be successfully engineered in E. coli.
- Biosynthetic devices can be purposefully regulated via transcription based control devices.
Motivations
Our project focused on engineering Escherichia coli to produce different compounds that smell fragrant. Since scents can both act as natural reporters and have a diverse array of applications, they represent a promising but thus far unexplored area of synthetic biology.
Future applications of this work that we envision include ...
- Improving the workplace environment for microbiologists working with Escherichia coli since E. coli produce a natural foul scent.
- Porting our system to bacterial species involved in bioremediation.
- Implementing our system in bacteria responsible for bad human odor in the mouth, armpits and feet.
Contributions
The following parts, devices, chassis, and systems have been designed, built, and tested to demonstrate that they work.
Parts
All of our parts are on the [http://partsregistry.org/cgi/partsdb/pgroup.cgi?pgroup=iGEM2006partsregistry.org/cgi/partsdb/pgroup.cgi?pgroup=iGEM2006&group=MIT registry].
Wintergreen (methyl salicylate):
- BBa_J45017: pchBA - proteins that generate salicylic acid
- BBa_J45004: BSMT - enzyme that converts salicylic acid to methyl salicylate
Banana (isoamyl acetate):
- BBa_J45008: BAT2 - enzyme that catalyzes the first step in isoamyl alcohol biosynthesis from L-leucine
- BBa_J45009: THI3 - enzyme that catalyzes the second step in isoamyl alcohol biosynthesis
- BBa_J45014: ATF1 - enzyme that converts isoamyl alcohol to isoamyl acetate
Control:
- BBa_J45992: osmY stationary phase promoter
Devices
- A biosynthetic device that converts salicylic acid to methyl salicylate (or wintergreen) (BBa_45100).
- A biosynthetic device that converts isoamyl alcohol to isoamyl acetate (or banana smell) (BBa_45200).
- A PoPS source that is only active during stationary phase (BBa_J45992).
- Stationary phase occurs when the cell culture reaches a sufficiently high density that growth slows due to lack of nutrients. Cell number tends to remain approximately constant.
- A PoPS source that is only active during exponential phase. The osmY stationary phase promoter was connected to the BBa_Q04401 inverter.
- Exponential phase is the growth stage where cells undergo their maximum rate of cell division.
Chassis
We have obtained from the Yale Genomic Stock Center, a strain of E. coli that does not have a noticeable smell (i.e. an indole knockout). This strain is the chassis of choice for all of our biosynthetic devices (BBa_J45999)
Systems
- Escherichia coli capable of producing a wintergreen scent autonomously (without addition of any precursors). (cotransformation of BBa_45300 and BBa_45180).
- E. coli capable of producing a banana scent autonomously (without addition of any precursors). (cotransformation of BBa_J45400 and BBa_J45250).
Characterization
- Smell test: Our systems definitely do smell nice!
- Stationary phase promoter: see [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J45992:Experience results] of connecting osmY promoter to GFP demonstrating that the stationary and exponential devices work as expected.
- Wintergreen generating device: see gas chromatography [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J45004:Experience results] demonstrating that our wintergreen generating device does in fact produce methyl salicylate in E. coli.
- No smell chassis: see gas chromatography [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J45999:Experience results] demonstrating that our indole knockout strain does not in fact produce indole.
Future work
In the future, we envision doing the following ...
- Porting the biosynthetic device that synthesizes isoamyl acetate to yeast to make banana bread.
- Porting the biosynthetic device that synthesizes methyl salicylate to Pseudomonas fluorescens, a species commonly used in bioremediation.
- Carrying out more extensive, quantitative characterization of our biosynthetic devices using gas chromatography.