ETH2006 copy
From 2006.igem.org
(→Duplexing by Concatenation) |
m (→PoPs duplexer device) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | →[[ETH Zurich 2006#System modeling|back to main page]] | |
| - | This device has two | + | == PoPS duplexer device == |
| + | |||
| + | This device has two PoPS outputs which in terms of activity should be duplicates of the input. | ||
PoPS duplexers are needed if we want to preserve the strict PoPS input/output interface of devices. | PoPS duplexers are needed if we want to preserve the strict PoPS input/output interface of devices. | ||
| Line 19: | Line 21: | ||
==== General Duplexer ==== | ==== General Duplexer ==== | ||
| - | The general duplexer variant offers most flexibility since both oututs can be controlled seperately. Ribosome binding sites of different strengths can be used to have different amplification factors on the ouptuts - which can be important if subsequent devices require input signals of different strengths. Another working point are the promoters, different promoter strengths also affect output signal strength. | + | The general duplexer variant offers most flexibility since both oututs can be controlled seperately. Ribosome binding sites of different strengths can be used to have different amplification factors on the ouptuts - which can be important if subsequent devices require input signals of different strengths. Another working point are the promoters, different promoter strengths also affect output signal strength. Note that some ribosome binding sites are missing in the illustration. |
==== Simplified Duplexer ==== | ==== Simplified Duplexer ==== | ||
| Line 25: | Line 27: | ||
==== Duplexing by Concatenation ==== | ==== Duplexing by Concatenation ==== | ||
| - | The | + | The direct way of PoPS duplexing is simple concatenation of two devices. The former device's output ends with the promoter - concatenation here means simply appending the inputs sequence (starting with ribosome binding site) of the subsequent device. Multiple input sequences of different gates can easily be appended. However, we loose the property of designated PoPS input/PoPS output boundaries for our devices. |
For simplicity, we have anyway decided to use concatenation for PoPS duplexing - at least for the first experiments. | For simplicity, we have anyway decided to use concatenation for PoPS duplexing - at least for the first experiments. | ||
| Line 42: | Line 44: | ||
| - | →[[ETH Zurich 2006# | + | →[[ETH Zurich 2006#System modeling|back to main page]] |
Latest revision as of 10:18, 30 October 2006
Contents |
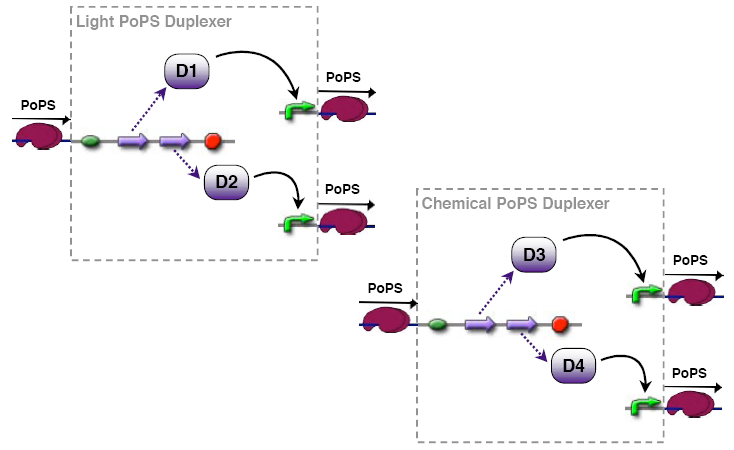
PoPS duplexer device
This device has two PoPS outputs which in terms of activity should be duplicates of the input.
PoPS duplexers are needed if we want to preserve the strict PoPS input/output interface of devices.
Implementation alternatives
| General Duplexer | Simplified Duplexer | Duplexing by Concatenation |
| PoPS Duplexer Variants | ||
General Duplexer
The general duplexer variant offers most flexibility since both oututs can be controlled seperately. Ribosome binding sites of different strengths can be used to have different amplification factors on the ouptuts - which can be important if subsequent devices require input signals of different strengths. Another working point are the promoters, different promoter strengths also affect output signal strength. Note that some ribosome binding sites are missing in the illustration.
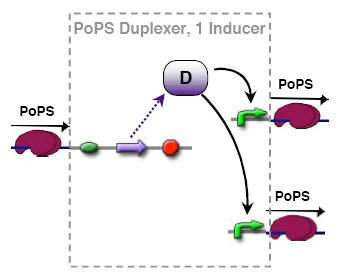
Simplified Duplexer
The simplified duplexer still facilitate specific output amplification, however, the only starting point is the promoters. Since both promoters are stimulated by the same activator, it might be more difficult to find appropriate promoters.
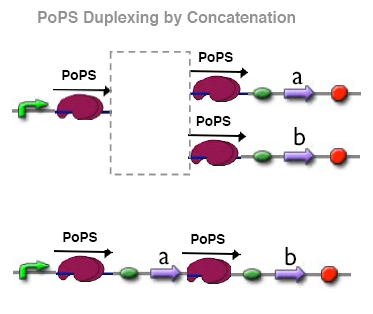
Duplexing by Concatenation
The direct way of PoPS duplexing is simple concatenation of two devices. The former device's output ends with the promoter - concatenation here means simply appending the inputs sequence (starting with ribosome binding site) of the subsequent device. Multiple input sequences of different gates can easily be appended. However, we loose the property of designated PoPS input/PoPS output boundaries for our devices.
For simplicity, we have anyway decided to use concatenation for PoPS duplexing - at least for the first experiments.